<<ach>>
<<ach>> is an electronic network for processing batches of debit and credit transactions between financial institutions in the USA. It is administered by the National Clearing House Association (NACHA).
The network can be used for the electronic transfer of funds between accounts. It is used for Direct Payment via <<ach>> (e.g. a recurring mortgage payments or an online consumer purchase) and Direct Deposit via <<ach>> (e.g. payroll payments, a refund made for an online purchase or a B2B payment).
The gateway allows you to process Direct Payments (payments) and Direct Deposits (refunds) via <<ach>>.
This page describes the requirements for processing <<ach>> payments via the <<paymentGateway>> and provides an overview of the payment flow and details about the supported <<webServicesIntegration>> operations for <<ach>> payments.
Prerequisites
You must have an <<ach>> account configured with an <<ach>> acquirer.
- You must obtain explicit customer authorization before <<ach>> settlement can take place.
- Since <<ach>> is not a real-time network, returns can still take place even after the payment request has been submitted to the <<paymentGateway>>.
- You must adhere to NACHA regulations. Compliance failure can carry substantial penalties. To keep up to date with current regulations, visit https://www.nacha.org/
- You must establish, implement and update policies, procedures and systems related to the initiation, processing and storage of entries, in order to:
- Ensure information confidentiality.
- Protect against threats to information security.
- Protect against unauthorized information use.
<<ach>> Data Flow
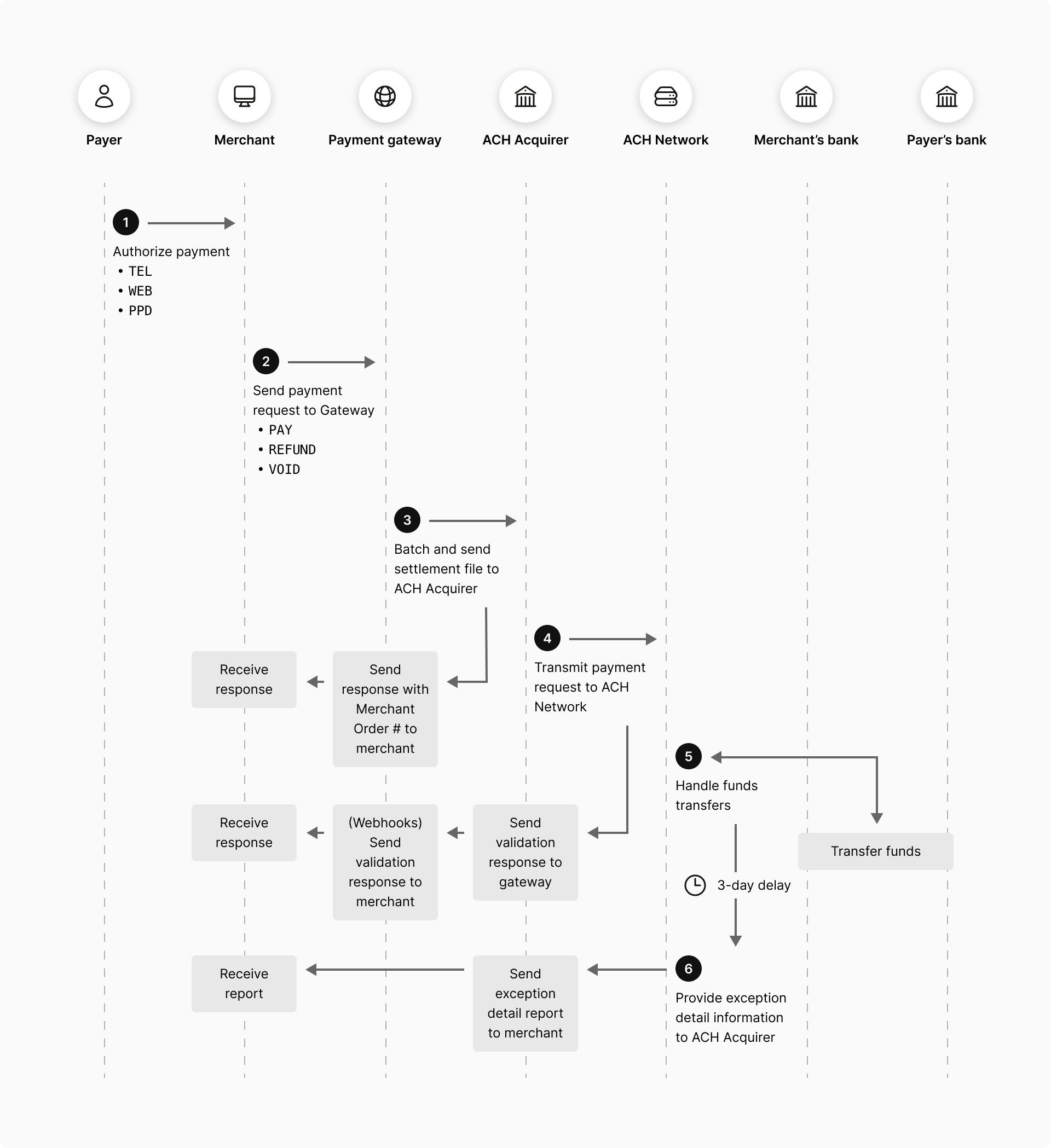
- The payer authorizes the payment or deposit.
NACHA-permitted Standard Entry Codes (SEC) are:
TEL. Telephone-initiated entry.WEB. Web-initiated entry.PPD. Prearranged payment and deposits.
- The merchant sends a transaction request to the <<paymentGateway>>.
Requests may be
PAY,REFUNDorVOID. - <<paymentGateway>> issues a response containing status information (e.g.
APPROVED_PENDING_SETTLEMENT).The transaction is added to the current batch for settlement.
The batch of transactions is closed in one of two ways:
- Once per day at the configured time.
- By you closing the currently-open batch by submitting an <<webServicesIntegration>>
CLOSE_BATCHrequest. Any subsequent transactions will be added to a new batch.
At the end of the day, all closed batches that have not yet been submitted are collected into a settlement file and transmitted to the <<ach>> Acquirer.
- The <<ach>> Acquirer issues an immediate response, containing the validation result of the transmitted data (e.g.
APPROVEDorDECLINED), and submits the payment requests to the <<ach>> network for processing.Notes:
- An
APPROVEDstatus issued by the <<ach>> Acquirer merely implies validated acceptance of the transmission for further processing; not an actual approval of the financial transaction. - To be notified of the <<ach>> Acquirer response, subscribe to Webhook Notifications.
- An
- The <<ach>> network manages the payment transactions between the applicable fincancial institutions.
- After a delay of up to 3 days, the <<ach>> Network sends an exception report of unapproved payment requests to the <<ach>> Acquirer, who will provide it for you .
Integrating <<ach>> payments
There are three options to integrate <<ach>> payments into your payment page:
If you have an existing <<checkout>> integration, you can use <<checkout>> to verify the <<ach>> payment details.
You can do this by setting interaction.operation=VERIFY in the Create Checkout Session request. <<checkout>> displays <<ach>> payments as a payment option to the payer. The data entered by the payer is verified using the verification methods supported by the configured acquirer.
You can determine the success of the verification operation by comparing resultIndicator to successIndicator. If the interaction was not successful, <<checkout>> displays a message indicating that verification has failed and prompts the payer to try again.
If you have your own payment page then you can choose the <<hostedSession>> integration option to have the <<paymentGateway>> securely capture the <<ach>> payment details and store them into a payment session.
<html>
<head>
<!-- INCLUDE SESSION.JS JAVASCRIPT LIBRARY -->
<script src="https://test-bankalfalah.gateway.mastercard.com/form/version/100/merchant/<MERCHANTID>/session.js"></script>
<!-- APPLY CLICK-JACKING STYLING AND HIDE CONTENTS OF THE PAGE -->
<style id="antiClickjack">body{display:none !important;}</style>
</head>
<body>
<!-- CREATE THE HTML FOR THE PAYMENT PAGE -->
<div>Please enter your Automated Clearing House details:</div>
<div>
<label class="control-label" id="ach-account-type-label">Account Type:</label>
<select class="form-control col-sm-6" name="ach-account-type" id="ach-account-type">
<option value="CONSUMER_SAVINGS">Consumer Savings Account</option>
<option value="CONSUMER_CHECKING" selected>Consumer Checking Account</option>
<option value="CORPORATE_CHECKING">Business Checking Account</option>
</select>
</div>
<div>Bank Account Holder: <input type="text" id="ach-account-holder" class="input-field" value="" readonly></div>
<div>Bank Account Number:<input type="text" id="ach-account-number" class="input-field" value="" readonly></div>
<div>Routing Number:<input type="text" id="ach-routing-number" class="input-field" value="" readonly></div>
<div><button id="payButton" onclick="pay();">Pay Now</button></div>
<!-- JAVASCRIPT FRAME-BREAKER CODE TO PROVIDE PROTECTION AGAINST IFRAME CLICK-JACKING -->
<script type="text/javascript">
if (self === top) {
var antiClickjack = document.getElementById("antiClickjack");
antiClickjack.parentNode.removeChild(antiClickjack);
} else {
top.location = self.location;
}
PaymentSession.configure({
fields: {
// ATTACH HOSTED FIELDS TO YOUR PAYMENT PAGE FOR ACH
ach: {
accountType: "#ach-account-type",
bankAccountHolder: "#ach-account-holder",
bankAccountNumber: "#ach-account-number",
routingNumber: "#ach-routing-number"
}
},
//SPECIFY YOUR MITIGATION OPTION HERE
frameEmbeddingMitigation: ["javascript"],
callbacks: {
initialized: function(response) {
// HANDLE INITIALIZATION RESPONSE
},
formSessionUpdate: function(response) {
// HANDLE RESPONSE FOR UPDATE SESSION
if (response.status) {
if ("ok" == response.status) {
console.log("Session updated with data: " + response.session.id);
} else if ("fields_in_error" == response.status) {
console.log("Session update failed with field errors.");
if (response.errors.bankAccountHolder) {
console.log("Bank account holder invalid.");
}
if (response.errors.bankAccountNummber) {
console.log("Bank account number invalid.");
}
if (response.errors.routingNumber) {
console.log("Routing number invalid.");
}
} else if ("request_timeout" == response.status) {
console.log("Session update failed with request timeout: " + response.errors.message);
} else if ("system_error" == response.status) {
console.log("Session update failed with system error: " + response.errors.message);
}
} else {
console.log("Session update failed: " + response);
}
}
}
});
function pay() {
// UPDATE THE SESSION WITH THE INPUT FROM HOSTED FIELDS
PaymentSession.updateSessionFromForm('ach');
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
- Include the
session.jsclient JavaScript library hosted by the gateway in your payment page. The path to this file includes both the api version and the merchant identifier for the session. - Create the HTML for the payment page containing the <<ach>> payment fields.
To prevent submission of sensitive data to the server, ensure the sensitive data fields arereadonlyand do NOT have thenameattribute. - Invoke
PaymentSession.configure(configuration)function.
The
configurationobject allows you to attach hosted fields to your payment page. You need to provide the following:
- session(optional), if you do not provide one, the client library creates a payment session.
- field selectors for <<ach>> payment fields, which when provided are replaced with corresponding proxy fields embedded in iFrames hosted by the <<paymentGateway>>. The proxy fields will have the same look and feel as the replaced fields.
-
mitigation option(s) for clickjacking prevention
Clickjacking, also known as a "UI redress attack", is when an attacker uses multiple transparent or opaque layers to trick a user into clicking on a button or link on another page when they were intending to click on the top level page. To use <<hostedSession>>, you must implement one or more of the following defenses against clickjacking attacks.
Frame Mitigation Option Implementation javascriptinclude "frame-breaker" JavaScript in your payment page. x-frame-optionsyour server should return an X-Frame Options HTTP response header. cspyour server should return Content-Security-Policy HTTP response header containing a frame-ancestors directive. You must specify which defenses are implemented via the
frameEmbeddingMitigationparameter in thePaymentSession.configure(configuration)call. For information on defending against clickjacking attacks, see Clickjacking Defense Cheat Sheet on the OWASP External Website. -
callbacks for handling various events during the <<hostedSession>> interaction
initialized( ): invoked when the hosted fields attach to your payment page.formSessionUpdate( ): invoked in response to thePaymentSession.updateSessionFromForm('ach')function (see next step)
- Invoke
PaymentSession.updateSessionFromForm('ach')to store the collected <<ach>> details into a payment session. Once the operation completes,formSessionUpdate( )callback is invoked with a result parameter. You must check theresult.statusvalue to determine if the operation was successful. See Handle Callback Responses. - You can use the returned payment session (session.id) to perform a tokenization or a payment transaction when required. For more information, see Perform an Operation Using the Session.
session.js Reference[JavaScript]
You can submit <<ach>> payment details directly to the <<paymentGateway>> using the following operations.
You initiate an <<ach>> payment by submitting an <<webServicesIntegration>>PAY request, and a refund by submitting an <<webServicesIntegration>>REFUND request.
Ensure that you include the following information in your request:
sourceOfFunds.type = ACH.sourceOfFunds.provided.ach.routingNumber: The payer's bank routing number.sourceOfFunds.provided.ach.bankAccountNumber: The payer's bank account number.sourceOfFunds.provided.ach.bankAccountHolder: The payer's account holder name.sourceOfFunds.provided.ach.accountType: The payer's bank account type.sourceOfFunds.provided.ach.secCode: The SEC code for the <<ach>> payment applicable to this transaction.The SEC code must be one of:
TEL: An <<ach>> Debit entry for a B2C payment authorized by the customer via the telephone. TEL may only be used when a relationship already exists between you and the payer or, when there is not an existing relationship, the payer initiates the contact with you.WEB: An <<ach>> Debit entry for a B2C payment authorized via the internet or a wireless network.PPD: An <<ach>> Debit or Credit entry based on an authenticated authorization provided by a payer. PPD is used for B2C payments (e.g. employee payroll, mortgage payments, or expense reimbursement).
You can void the previous transaction on an order by submitting an <<webServicesIntegration>>VOID request for the order with the target transaction ID parameter referencing the PAY or REFUND request.
For a successful <<webServicesIntegration>>VOID request, the referenced target transaction is removed from the batch and therefore will not be submitted to the <<ach>> Acquirer.
Transactions can no longer be voided once the batch containing the referenced target transaction has been closed for settlement (i.e. settlement is in progress) or has already been settled.
You can verify the payment details for an <<ach>> payment by submitting an <<webServicesIntegration>>VERIFY request.
Currently, the <<paymentGateway>> only supports semantic verification of the ACH payment details, but does not verify that the account is a valid bank account and the bank participates in <<ach>>.
Batch management and settlement
You can control batch closure by submitting an <<webServicesIntegration>>CLOSE_BATCH request with the acquirer ID for your <<ach>> acquirer. The acquirer ID is provided in transaction.acquirer.id in the transaction response.
As a result, the current <<ach>> Acquirer batch in the <<paymentGateway>> will be closed. Subsequent <<ach>> transactions will be added to a new the <<paymentGateway>>-internal batch.
Reconciliation
The Retrieve Transaction response for successful <<ach>> transactions contains the identifier for the transaction that the acquirer uses in transaction.receipt.
This identifier will be used in the Exception Detail Report provided by the Paymentech Salem <<ach>> acquirer. This contains all unsuccessful <<ach>> transactions and can be used to reconcile your payments.
The transaction status provided by the gateway (response.gatewayCode) is not updated with the actual response from the <<ach>> network.
Testing <<ach>> transactions
You can test your integration using your TEST merchant profile.
The <<paymentGateway>> provides an emulator that will return a response with response.gatewayCode=APPROVED for all valid requests for <<ach>> payments.